User Guide
Developers
Fields

Understand the role of fields and how to handle them.
About Fields
Fields are like columns in a spreadsheet. They store different types of data like text, numbers, or dates. Fields can be standard (built-in) or custom (the ones you create).
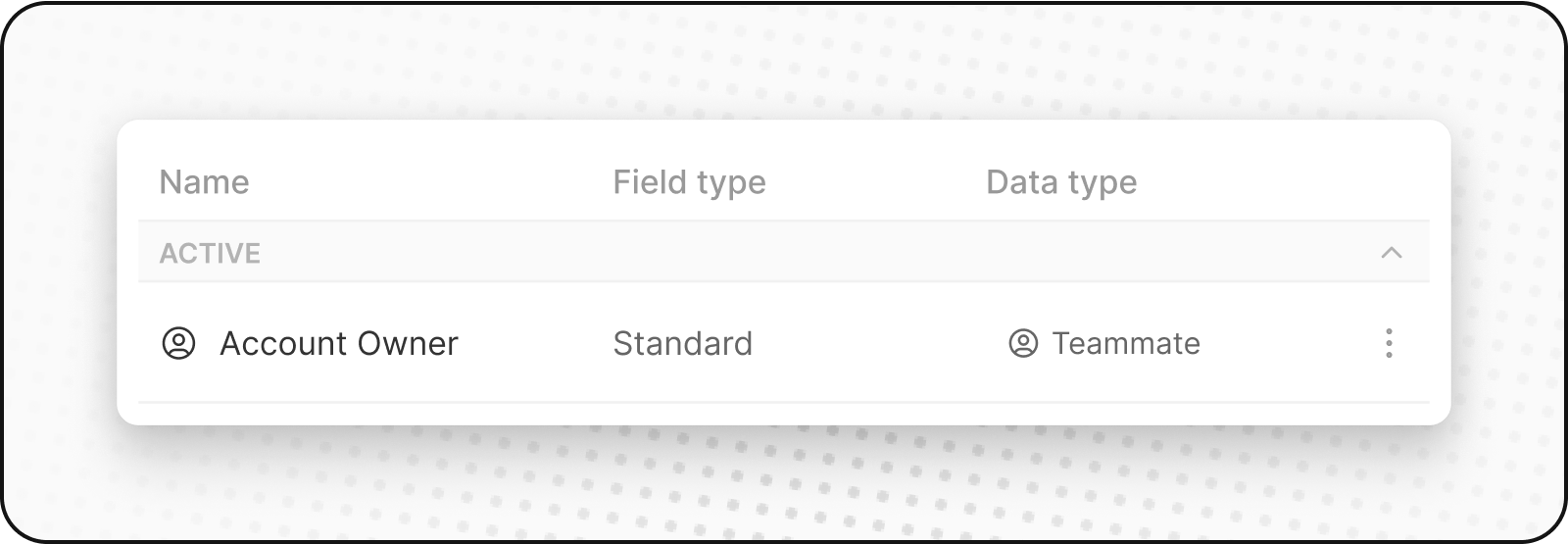
Standard Fields
Standard fields come built-in with Twenty to handle common business needs.
For example, First Name and Last Name are standard fields in the People object. They store text data for individual names.
You cannot delete standard fields, but you can deactivate them if you don't need them.
You can also customize the options of the standard SELECT type fields, for example the options for the Stage on Opportunities.
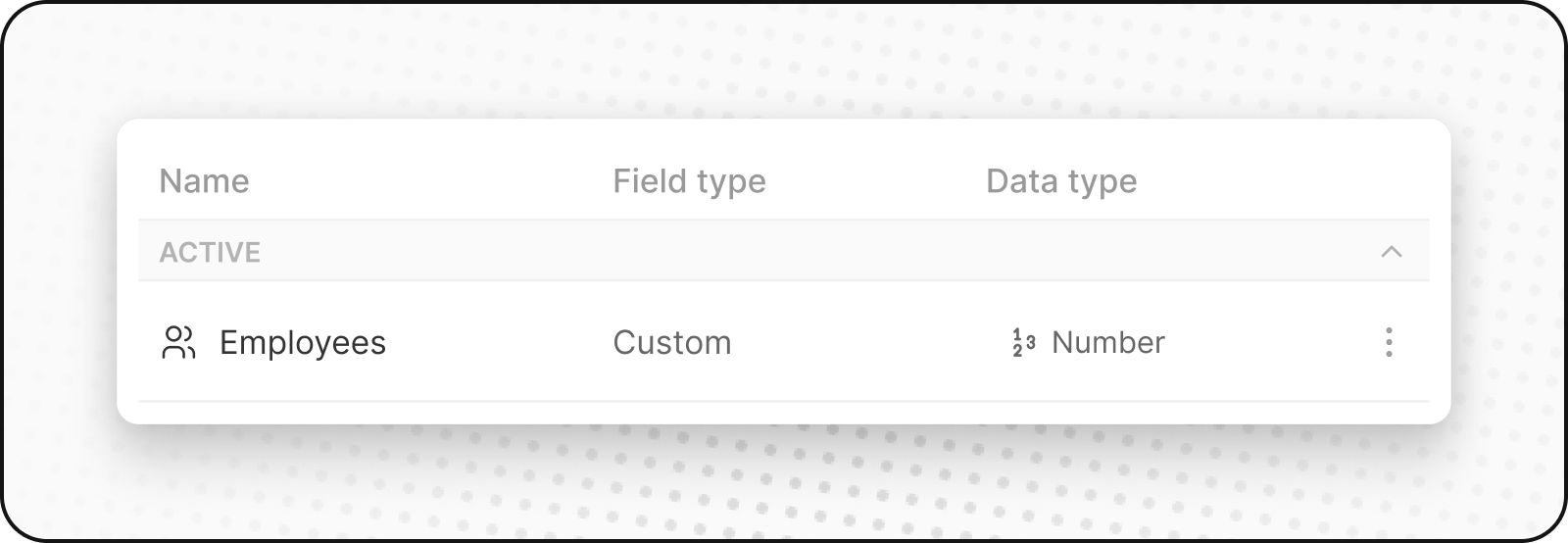
Custom Fields
Custom fields can be added to any object. You can store text, numbers, dates, dropdown selections, and more. Use custom fields to track information that's specific to your business.
For instance, a custom field for SpaceX could be Rocket Active Status, indicating if a rocket is operational.
Create a Custom Field
To add a custom field to any object, follow these steps:
- Go to
Settingsin the left sidebar. - Go to
Data Model, then select the object you wish to customize. - Proceed by clicking on
Add Field. - Choose a field name and type that suits your requirements. Consider adding a field description for better understanding.
Your newly created field is now available within the application's fields. To display it on a specific view, click on the options menu, then select Fields.
Quick way: Click the + button at the top right of any object table, then select Customize fields. This takes you directly to the Data Model settings.
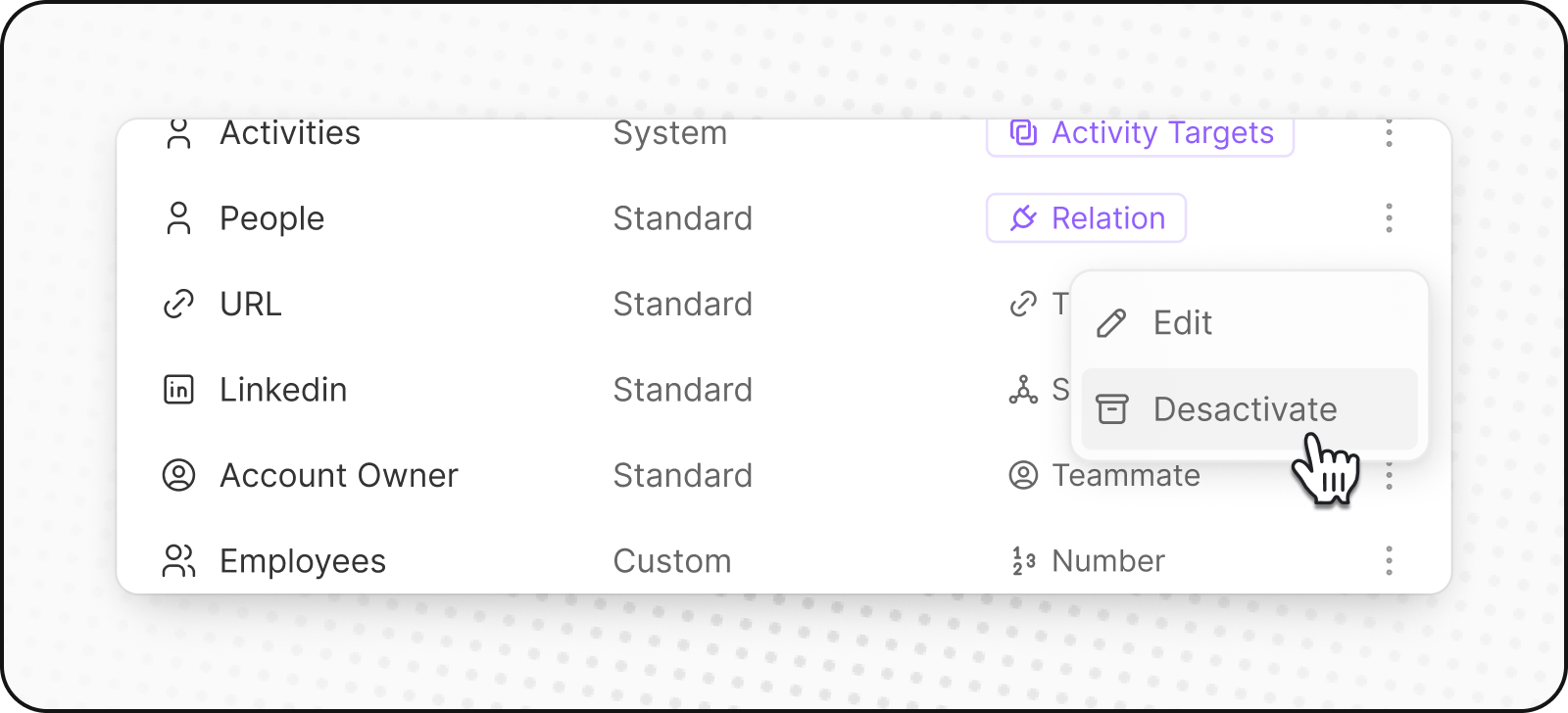
Deactivate a field
You can deactivate a field to hide it from the app without losing your data. Think of it as hiding the field rather than deleting it.
Here's how you can do it:
-
Find the field you want to deactivate in your object settings.
-
Click the three dots
⋮next to the field to open the menu. -
Select
Deactivatefrom the dropdown.
What happens when you deactivate a field?
-
In the app: The field disappears and you can't add new values to it.
-
Existing relationships: If it's a relation field, existing connections stay but you can't create new ones.
-
API access: You can still access the field and its data through the API.
You can reactivate Standard and Custom Fields or have the option to permanently delete them.
Make Fields Unique
Make a field unique to ensure distinct records cannot have the same value. For example, email addresses are unique for each person.
If you get an error when setting uniqueness, check for duplicate values in your data (including deleted records).
Field Configuration Best Practices
Naming Conventions and Limitations
- Relation field names cannot be updated after creation (impacts API structure)
- Singular and plural named must be distinct: Our GraphQL API needs distinct names for mutations
- Protected field names: some names are reserved for system usage (e.g.,
Type)
Currency and Phone Fields
- Default currency: can be configured via the data model
- Default country codes: can be configured for phone fields via the data model
Select Fields
- A default option can be selected for each Select field
Record Text Fields
- Each object has one main display field: This field appears in the leftmost column and represents the record when linked to other objects. It must be a text field. For example, People uses
Nameas the main field, so when you link a person to a company, you'll see their name in the company's view.
Relation Fields
- Connect objects together: Relation fields link records from different objects. For detailed information on creating and managing relationships, see our Relation Fields article.
Noticed something to change?
As an open-source company, we welcome contributions through Github. Help us keep it up-to-date, accurate, and easy to understand by getting involved and sharing your ideas!
